The ocean plays a particular role in the climate system acting as significant sink of atmospheric heat and CO 2. It works by adding finely ground iron into the ocean which stimulates photosynthesis in phytoplanktons.
 Engineering Com Ocean Acidification Combatted By Canadian Google Science Fair Finalist
Engineering Com Ocean Acidification Combatted By Canadian Google Science Fair Finalist
This is called ocean acidification.

Ocean acidification solutions. July 19 2018. The issue of ocean acidification is the decreased production of the shells of shellfish and other aquatic life with calcium carbonate shells. Finally leads to ocean acidification.
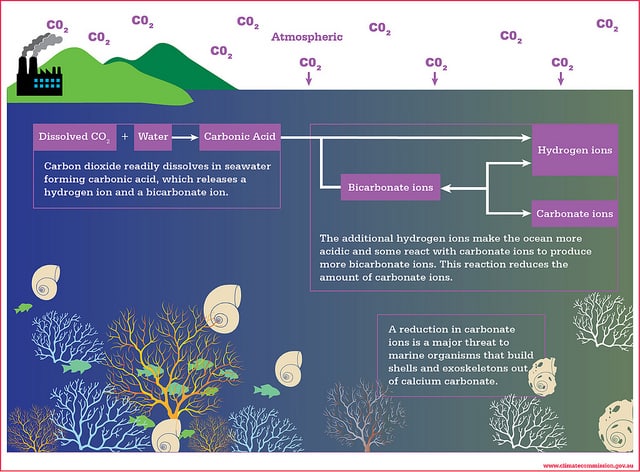
Under a lower pH ocean future increasing numbers of calcium carbonate fixing organisms could face dramatic losses or even extinction. Carbon dioxide released from the burning of fossil fuels dissolves in seawater and produces carbonic acid and this lowers the pH of the ocean water. An increase in H ions leads to lowering the oceans pH or causing ocean acidification.
Ocean acidification is a direct consequence of increased human-induced carbon dioxide CO 2 concentrations in the atmosphereThe ocean absorbs over 25 of all anthropogenic emissions from the atmosphere each year. The ocean absorbs around 30 of carbon dioxide CO 2 released to the atmosphere as a result of human activities. There have been proposals to soak up the oceans excess acid by throwing iron limestone or olivine into the water boosting plankton growth adding the building blocks for shells or chemically absorbing CO2.
As CO 2 dissolves in seawater it forms carbonic acid decreasing the oceans pH. EPAs Ocean and Coastal Acidification Program promotes awareness and conducts research and long-term monitoring to mitigate impacts of acidification and develop solutions. Bren Smith an ocean farmer believes that kelp farming is the future.
States play a critical role in guarding their coastlines against local causes of acidification. The phytoplankton converts the oceans dissolved carbon. Chaired by Professor Dan Laffoley and Dr John Baxter IUCN WCPA the Ocean Acidification International Reference User Group OA-iRUG has been created as a forum to help convey scientific results on ocean acidification research programmes to non-scientific audiences and science end-users in particular policy and decision makers.
Ocean Currents Seeking Creative Solutions to Ocean Acidification Paul Williams Shellfish Management Policy Advisor for the Suquamish Tribe in Washington State discusses the impacts of ocean acidification in the Pacific Northwest and the challenges for future generations. Over the last decade there has been much focus in the ocean science community on studying the potential impacts of ocean acidification. Fifty years ago the native oyster population could filter the entire Chesapeake in five days.
It also aims to highlight areas for further action to address. The consistent decrease of PH level of ocean water is called ocean acidification. Take oysters for example.
Secondly ocean acidification also impacts organisms that dont fix calcium carbonate. But fishing and disease outbreaks have reduced oysters to just 1 of their historic population. C a rbon dioxide absorption into the ocean.
Seawater is slightly basic meaning pH 7 and ocean acidification involves a shift towards pH-neutral conditions rather than a transition to acidic conditions pH 7. The most effective way to limit ocean acidification is to act on climate change implementing solutions to dramatically reduce the use of fossil fuels. If we dramatically cut our global warming emissions and we limit future warming we can significantly reduce the harm to marine ecosystems.
As CO 2 dissolves in sea water it forms carbonic acid thereby decreasing the oceans pH leading to a suite of changes collectively known as ocean acidification. NOAAs Ocean Acidification Program serves to build relationships between scientists resource managers policy makers and the public in order to research and monitor the effects of changing ocean chemistry on economically and ecologically important. An adult oyster is capable of filtering 25-50 gallons of water a day.
This would reverberate throughout the marine food chain as key links were diminished or extinguished. This has caused the additional hazard of ocean acidification. The acidity of the ocean has.
The idea is a smaller gentler cousin to grander schemes of geo-engineering.