Impact points associated with ocean acidification eg reduced reef rugosity coralline. Climate change and ocean acidification imperil fisheries sweeping IPCC report says Human-driven climate change has made the oceans hotter and more acidic depleting them of oxygen and kneecapping their ability to produce life a trend that will only continue if.
 Climate Change And Ocean Acidification At Gray S Reef National Marine Sanctuary
Climate Change And Ocean Acidification At Gray S Reef National Marine Sanctuary
In these areas wind-driven upwelling brings colder nutrient- and carbon-rich water to the surface.

Climate change and ocean acidification. While this uptake provides a valuable service to human societies by moderating the rate and severity of climate change it comes at a cost for the oceans. Ocean Acidity This indicator describes changes in the chemistry of the ocean that relate to the amount of carbon dioxide dissolved in the water. Ocean acidification is one aspect of global climate change.
Ocean acidification affects marine life Coastal and marine ecosystems are under tremendous stress from climate change. Ocean acidification refers to decreasing levels of pH in the ocean which makes the sea more acidic. Human-caused emissions of carbon dioxide fundamentally change the.
This causes changes in water temperature ocean acidification and deoxygenation leading to changes in oceanic circulation and chemistry rising sea levels increased storm. Globally ocean acidity has already increased by 30 compared with pre-industrial times over 200 years ago. This is because climate change such as warming and freshening of the oceans is acting in tandem with the enormous oceanic uptake of C02 said Bellerby.
While the full impacts of climate change on the oceans are unclear studies predict increasing temperatures rising sea levels and changes to the ocean chemistry such as ocean acidification among others. Canadian Parks and Wilderness Society. Ocean acidification is the change in seawater chemistry due to the absorption of increasing carbon dioxide CO 2 in the air from fossil fuels and deforestation.
Ocean Carbon Dioxide Levels and Acidity 19832015. A changing climate means a changing ocean. It is the long-term change in seawater chemistry due to the absorption of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
In this review we examine marine macro-autotroph biochemistry and physiology relevant to their response to elevated. The ocean is being disproportionately impacted by increasing carbon dioxide CO 2 and other greenhouse gas emissions GHG from human activities. Roughly 30 percent of human-made CO2 is absorbed by the oceans.
Although seagrasses and marine macroalgae macro-autotrophs play critical ecological roles in reef lagoon coastal and open-water ecosystems their response to ocean acidification OA and climate change is not well understood. Ocean acidification paired up with other climate impacts like warming waters deoxygenation melting ice and coastal erosion pose real threats to the survival of many marine species. This is happening at an unprecedented rate and will continue unabated if we dont stop burning dirty fossil fuels.
Significant changes to ocean stratification and circulation can also be observed regionally along the eastern ocean boundaries and at the equator. The ocean and climate change. That will be bad.
Climate change refers to change in global patterns of the atmosphere and ocean while ocean acidification is the decline in ocean pH and related variables. This upwelled water is more efficient in heat and anthropogenic CO 2 uptake. Over the last decade there has been much focus in the ocean science community on studying the potential impacts of ocean acidification.
Arctic ocean acidification is happening at a faster rate than found in other global regions. Both effects are due in large part to the buildup of anthropogenic carbon dioxide in the atmosphere mainly resulting from burning fossil fuels. Climate change is projected to profoundly impact coastal and marine ecosystems and is expected to have significant effects on sea temperature sea level storm intensity and ocean chemistry.
Some anticipated changes are more damaging storms more extreme floods and droughts and a northward shift in the ranges of at least some species. The oceans have absorbed between 24 and 33 of anthropogenic carbon dioxide CO2 emissions during the past five decades. With more and more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere oceans absorb more and more of it becoming you guessed it more and more acidic.
Climate Change and Ocean Acidification Olympic Coast The Juan de Fuca Eddy also called the Big Eddy can be influenced by changes in wind and current patterns due to climate change. Ecological feedback processes on a coral reef showing pathways of disturbance caused by climate change. The IAEA supports Member States in using nuclear and isotopic techniques to develop a science-based.
The Eddy is a seasonal feature that entrains nutrient-rich cold water. But climate change isnt the only consequence of carbon pollution so is ocean acidification. Ocean Acidification Will Make Climate Change Worse As we emit more carbon dioxide the oceans will become more acidic.
Anything we do to mitigate climate change today will benefit the future of the ocean as well.
 Ocean Acidification Is Much More Harmful Than Previously Thought Intelligent Living
Ocean Acidification Is Much More Harmful Than Previously Thought Intelligent Living
 12 Ocean Acidification Ideas Ocean Acidification Ocean Global Warming
12 Ocean Acidification Ideas Ocean Acidification Ocean Global Warming
 What Is Ocean Acidification Climate Science And Climate Change
What Is Ocean Acidification Climate Science And Climate Change
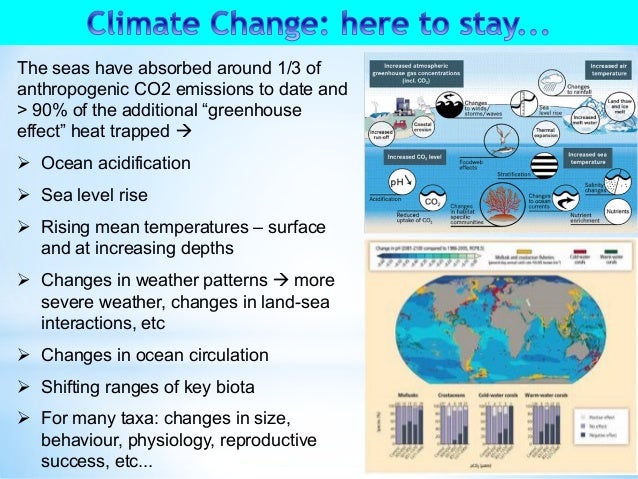 Potential Impacts Of Climate Change And Ocean Acidification For The F
Potential Impacts Of Climate Change And Ocean Acidification For The F
 Ocean Acidification National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
Ocean Acidification National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
Ocean Acidification Beachapedia
 Climate Change Indicators Ocean Acidity Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
Climate Change Indicators Ocean Acidity Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa
 Coral Reefs Under Rapid Climate Change And Ocean Acidification Science
Coral Reefs Under Rapid Climate Change And Ocean Acidification Science
 Ocean Acidification A Hidden Impact Of Climate Change Navigating Nature
Ocean Acidification A Hidden Impact Of Climate Change Navigating Nature
 Ocean Acidification Will Make Climate Change Worse Time Com
Ocean Acidification Will Make Climate Change Worse Time Com
 Ocean Acidification And Observations Itw Alexander Venn Explore To Understand Share To Bring About Change
Ocean Acidification And Observations Itw Alexander Venn Explore To Understand Share To Bring About Change
 Ocean Acidification Process Climate Central
Ocean Acidification Process Climate Central


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.